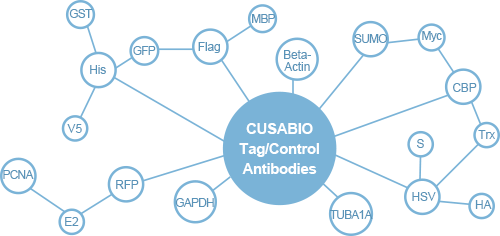
Cusabio Tag Recombinants
Tag antibodies
Tag antibodies can be used for the detection and purification of multiple proteins with the same tag. When certain target proteins cannot be immunoprecipitated without specific antibodies, an epitope can be used to tag the protein and then a tagged antibody is selected for this epitope so that immunoprecipitation can continue. With the rapid development of proteomics, the use of tag recombinant proteins has increased considerably in recent years. Recombinant hybrids contain affinity tags such as GST, Myc, His, etc., which can be used to help target protein purification, which has been widely used.
Load control antibodies
Loading control antibodies are used to assess Western blot efficiencies and compare the amounts of protein loaded in each well on a gel so you can determine equal loading and sample quality. It is important to use loading controls to determine protein expression and interpret Western blot results. Some common loading checkpoint antibodies include beta-actin, GAPDH, histone H3, alpha-tubulin, beta-tubulin, etc.
The importance of loading quality control antibodies cannot be overstated. If your load control is questionable, all of your results can be questioned. And CUSABIO is here to ease your worries. CUSABIO offers a wide selection of monoclonal loading control antibodies, including GAPDH, α-tubulin, and β-actin for various species. We also have some conjugated control antibodies, such as HRP or biotin-conjugated control antibodies.
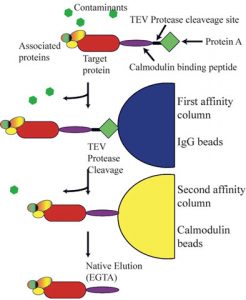
The characteristics of CUSABIO label/control antibodies
- The diversity of Labels and Controls
- High sensitivity: detects lower expression levels
- Higher reliability: the small difference between batches
- Multiple Validations
- Western Blot (WB)
- Flow cytometry (FC)
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Immunofluorescence (IF)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
What is a tagged antibody? What are tag antibodies used for?
A tag, or an epitope tag, is an antigenic sequence, such as a protein or a polyhistidine, that is determinant for the binding of a special antibody, which determines the specificity of an antigen. The tag is usually added to a protein of interest by genetic engineering, forming a fusion protein that is detected by a corresponding antibody. Antibodies that specifically recognize and bind to these tag epitopes are called epitope tag antibodies or tag antibodies.
When specific antibodies are not available for detection of the protein of interest, tagged antibodies are an alternative and are necessary. Tag antibodies are used for protein isolation and purification, monitoring protein expression and localization, protein-protein interactions. Some common experiments, such as ELISA, Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation, often use different label antibodies. For more details on tag antibodies, please read this article: Tag Antibodies, Your Good Partner in Protein Research.
What is a loading control antibody? What are loading control antibodies used for?
Control antibodies, as the name implies, are a series of internal control antibodies. They are specific for a highly expressed protein and constitutively. In general, control antibodies can be divided into two groups, including isotype control antibodies and loading control antibodies. The best loading control antibody should be consistently and stably expressed in different tissues and under different physiological and pathological conditions. Housekeeping proteins are often ideal candidates for loading control antibodies.
Loading control antibodies are necessary to obtain accurate expression data on Western Blot. They are responsible for monitoring target proteins in the Western Blot, confirming uniform sample loading and gel-to-membrane transfer that causes more intense staining at the edge of the blot, and guarding against “edge effect” to normalize results. results. Loading control antibodies can also be used to detect whether a variation in protein loading has occurred and can interpret observed variations in the target band(s).